In Odoo 18, costing methods are essential for inventory management because they determine how the value of products in stock is recorded and maintained. The chosen costing method directly affects the valuation of stock on hand, which in turn has a significant impact on financial indicators such as net profit, gross income, and working capital. ERP systems like Odoo 18 make costing easier by automating the process instead of relying on manual records.
Odoo offers mainly 3 costing methods
- Standard Costing Method
- Average Costing Method
- First In First Out (FIFO)
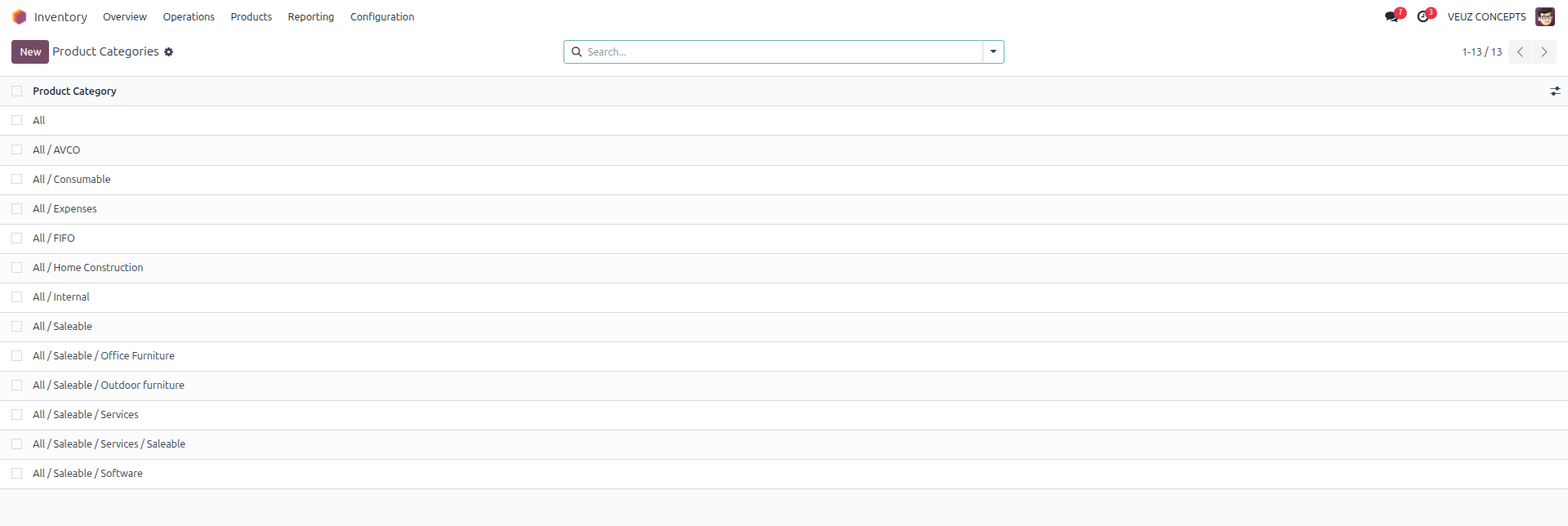
Now lets see how various costing methods are working in Odoo. The setup of costing methods is done through the configuration of the Product Category.
Inventory > Configuration > Product Category
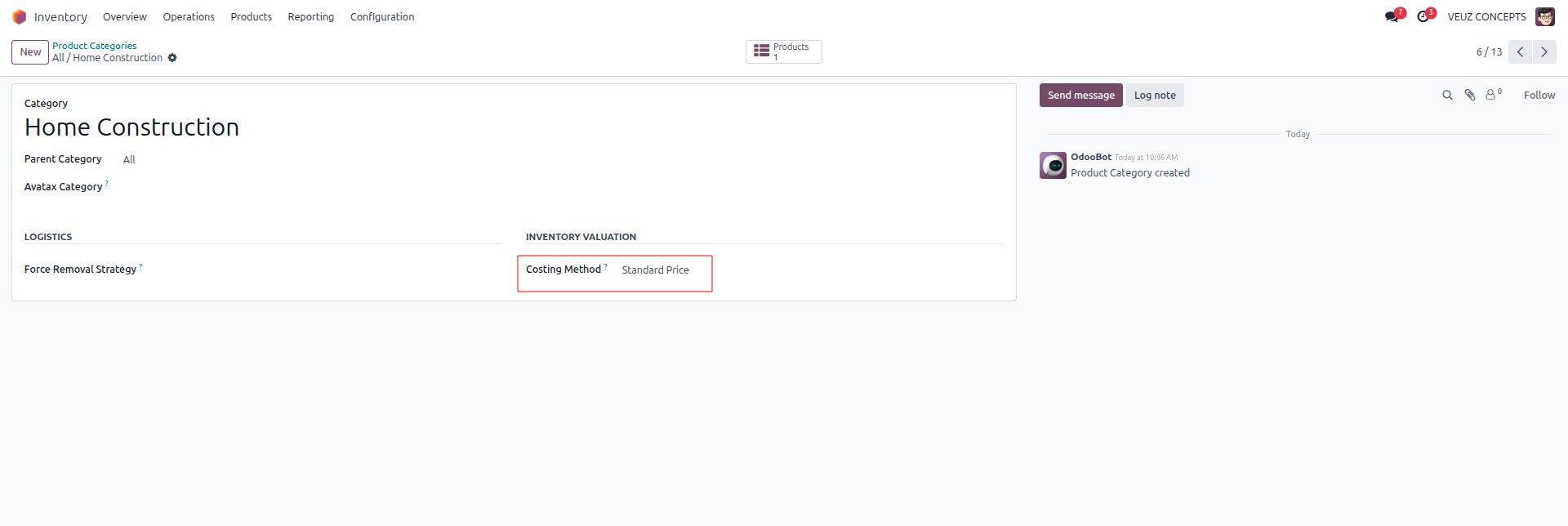
Standard Costing Method
In Odoo 18, Standard Costing Method also referred to as the "Standard Price" method is a straightforward and effective way to manage inventory valuation and costing. Standard Price is considered as the default costing method, and in this costing method you can give a fixed price for your product & this fixed price will be used throughout the valuation. Ideal for sectors like furniture, machinery, and textiles that have steady, predictable costs. Aids in keeping budgeting and pricing consistent.
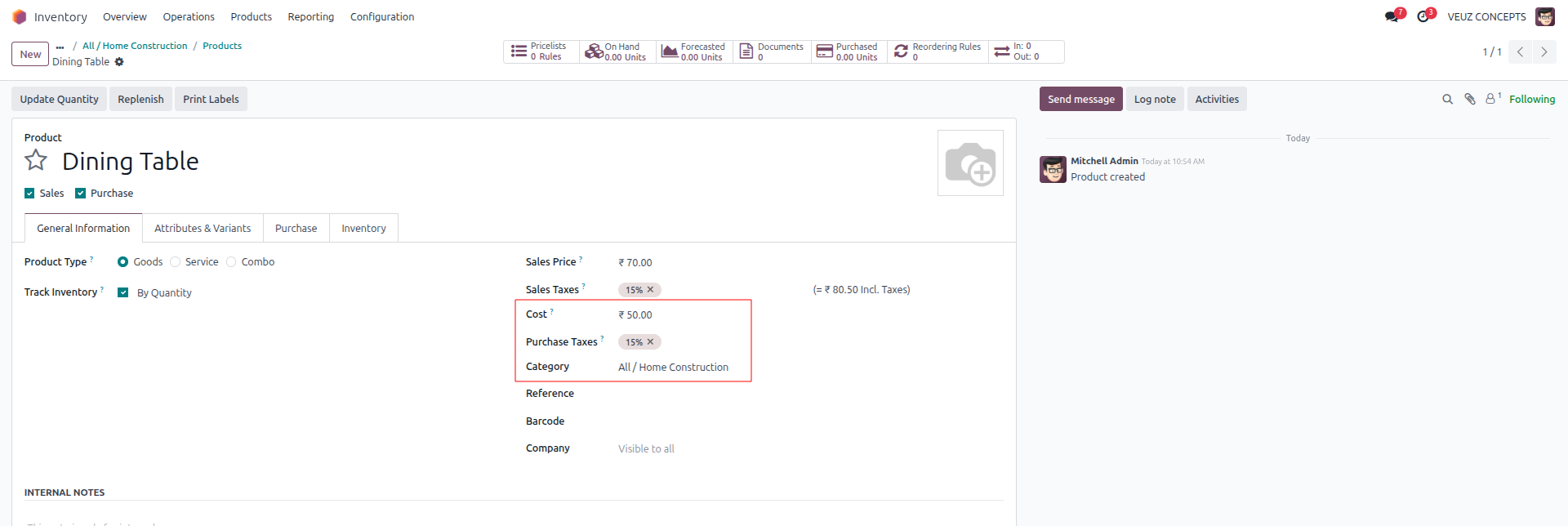
Let's see the working further with an example. For that let's create a new Product with cost 50 SR and product category as the selected “All/Home Construction”.
Now, let’s create a purchase order for the same product, setting the unit price to 60 SR for a quantity of 10 units.
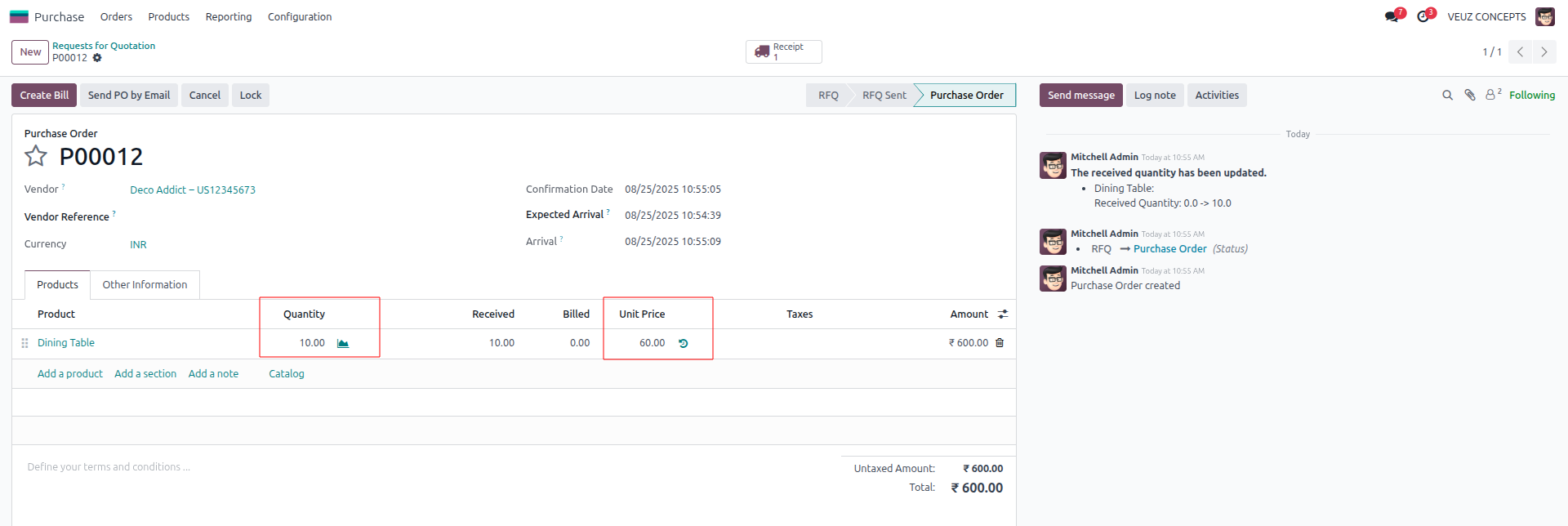
After confirming and validating the purchase order, we can review the inventory valuation.
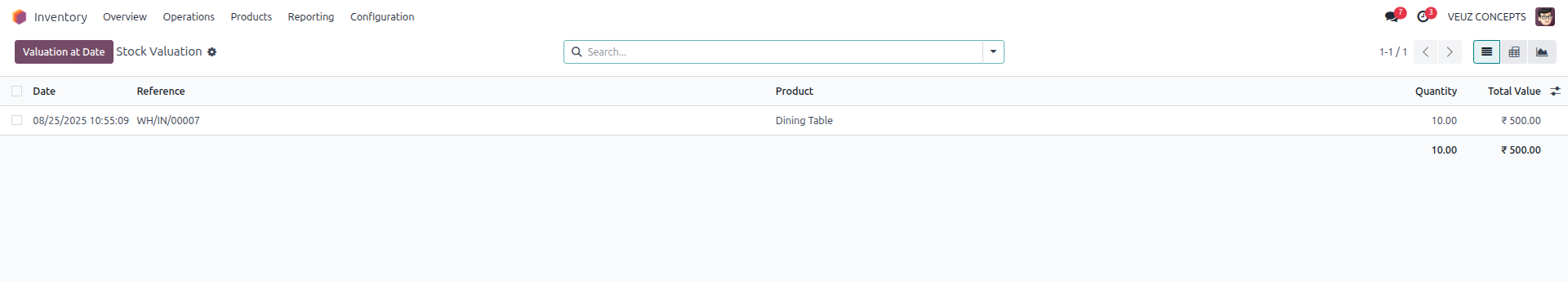
In the purchase order the product "Dining Table" was purchased for 60 SR per unit, but the inventory valuation shows that the unit price is still 50 SR,which is the product's standard cost. Businesses that value consistency and ease in inventory valuation are the best candidates for Odoo Standard Pricing. Because the product cost remains constant despite fluctuations in purchase prices, it provides stability for planning, budgeting, and setting sales prices.
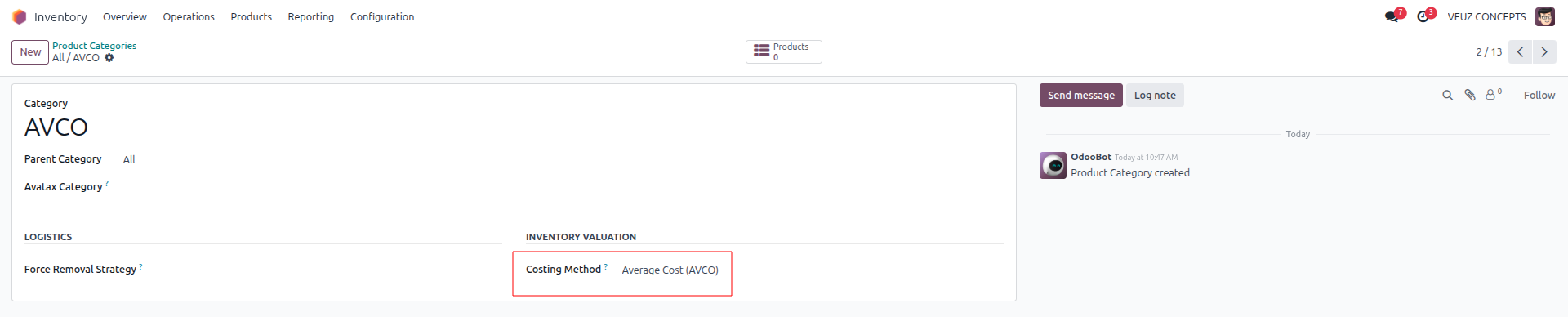
Average Costing Method
In the Average Costing method the average of the product's purchase costs is used to determine its value. This implies that the average cost and total product valuation are automatically modified each time you purchase more in different quantities at various prices. Best for businesses that purchase the same product at varying prices and quantities (e.g., electronics, wholesale trading). Smooths out cost fluctuations.
Lets see the working further with an example. For that let's create a new Product with cost 200 SR and product category as the selected “All/AVCO”.
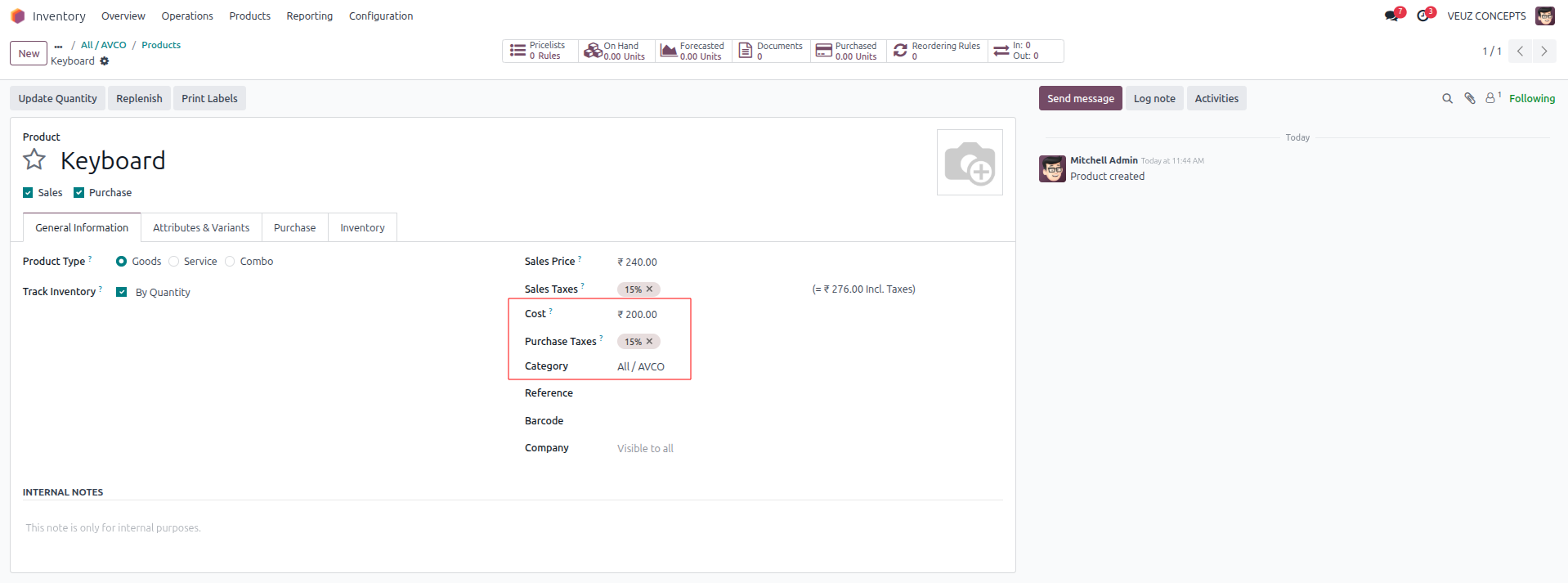
Now, let’s create 2 purchase orders for the same product, setting the unit price to 200 SR and 220 SR and quantity 1 unit and 3 units respectively.
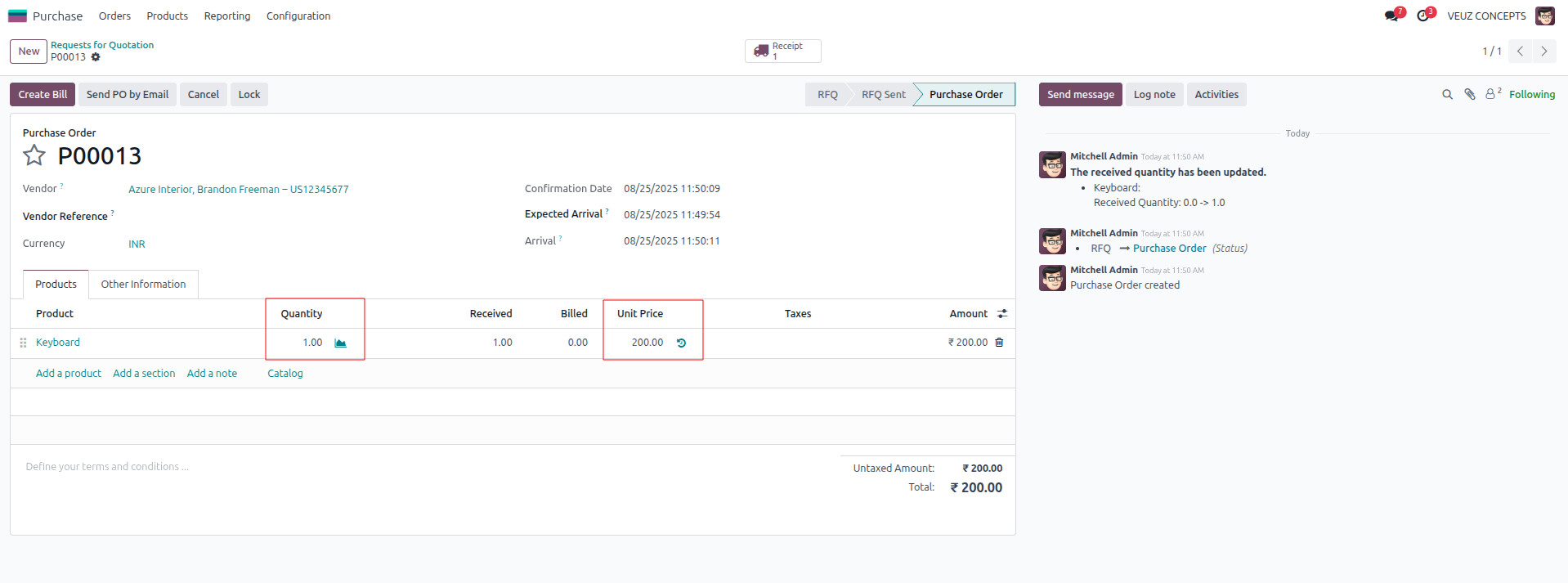
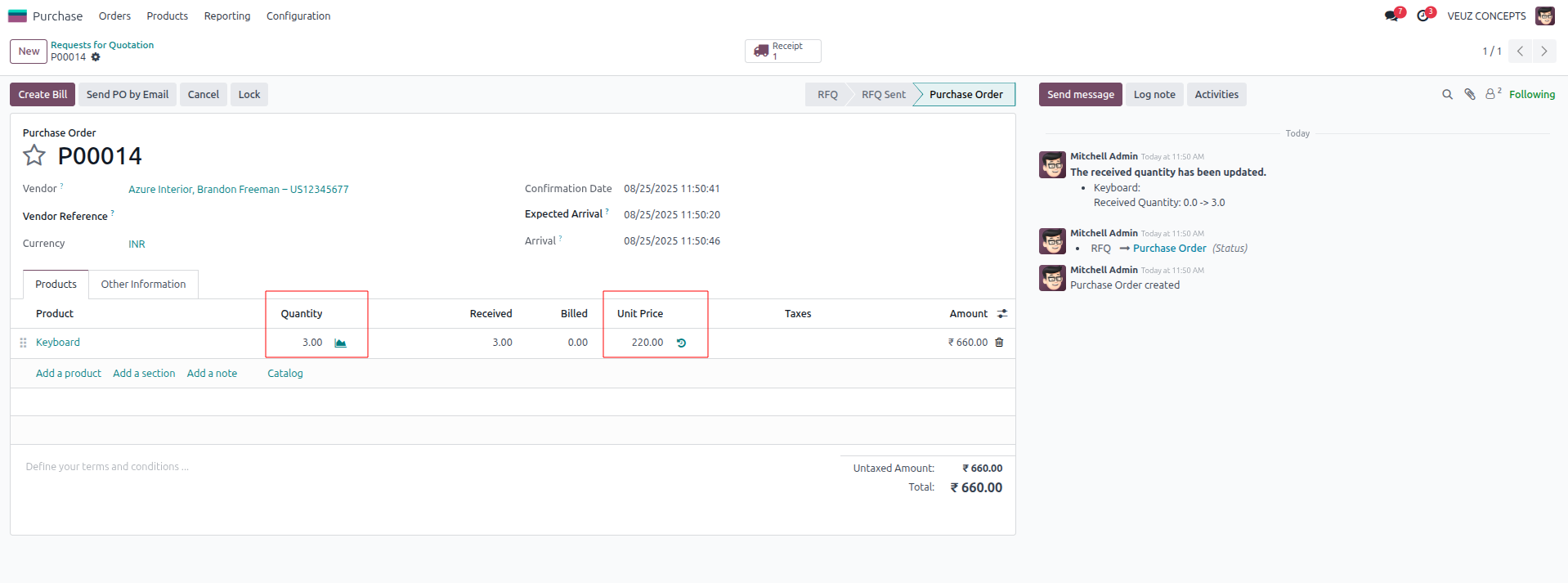
After confirming and validating the purchase order, we can review the inventory valuation.
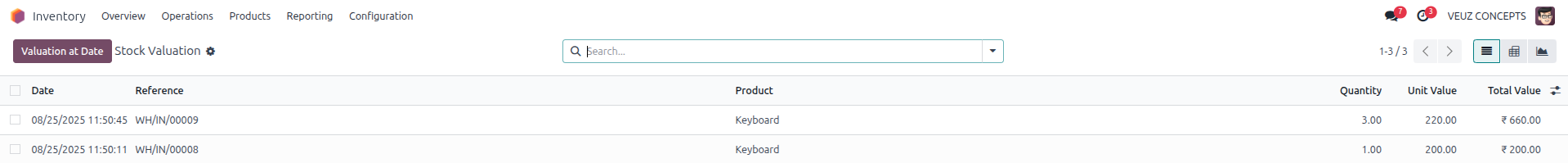
At first, one unit was purchased for 200 SR, so the stock value and the average cost per unit was 200 SR. Later, three more units were purchased at 220 SR each, adding 660 SR to the stock value. This brought the total stock value to 860 SR for four units in total. When 860 SR is divided by four, the new average cost per unit becomes 215 SR. Thus, under the Average Costing method, all four units are valued at 215 SR each.
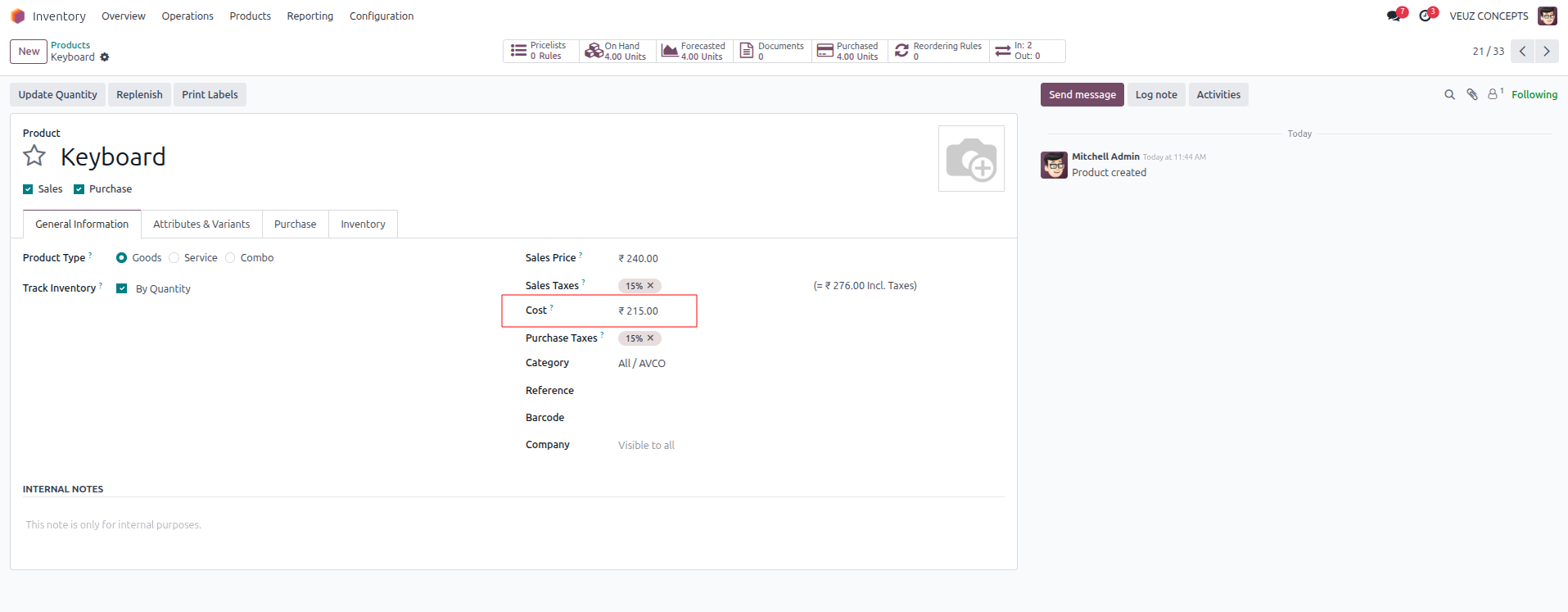
First In First Out (FIFO)
The Products that are purchased first should be sold first and this product cost is tracked in real time basis on the actual purchase prices. Ideal for items with shelf life or regulatory requirements (e.g., food, beverages, medicines).
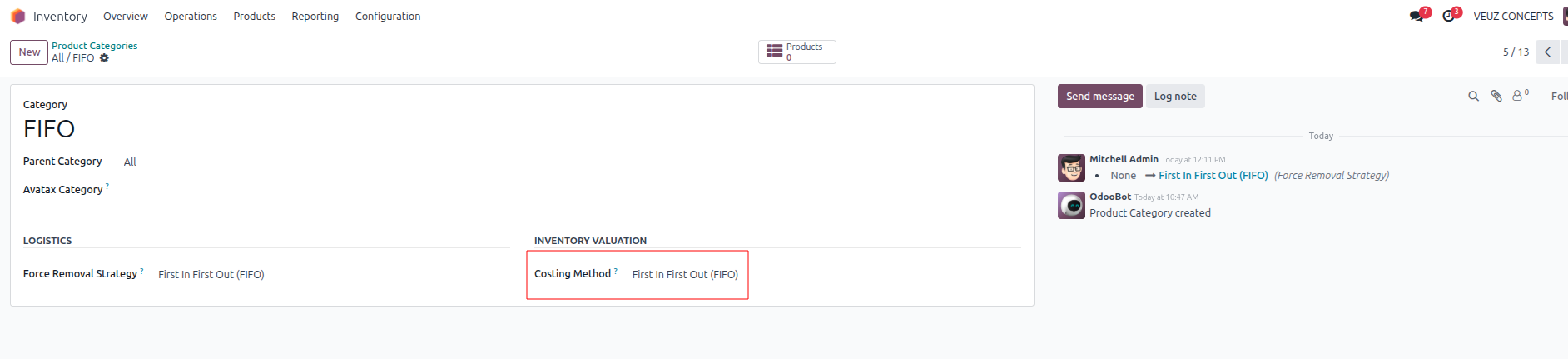
FIFO can be applied by setting the product category to use First In, First Out for both costing and stock removal. Next, create a product under the category “All/FIFO” and generate purchase orders for that product.
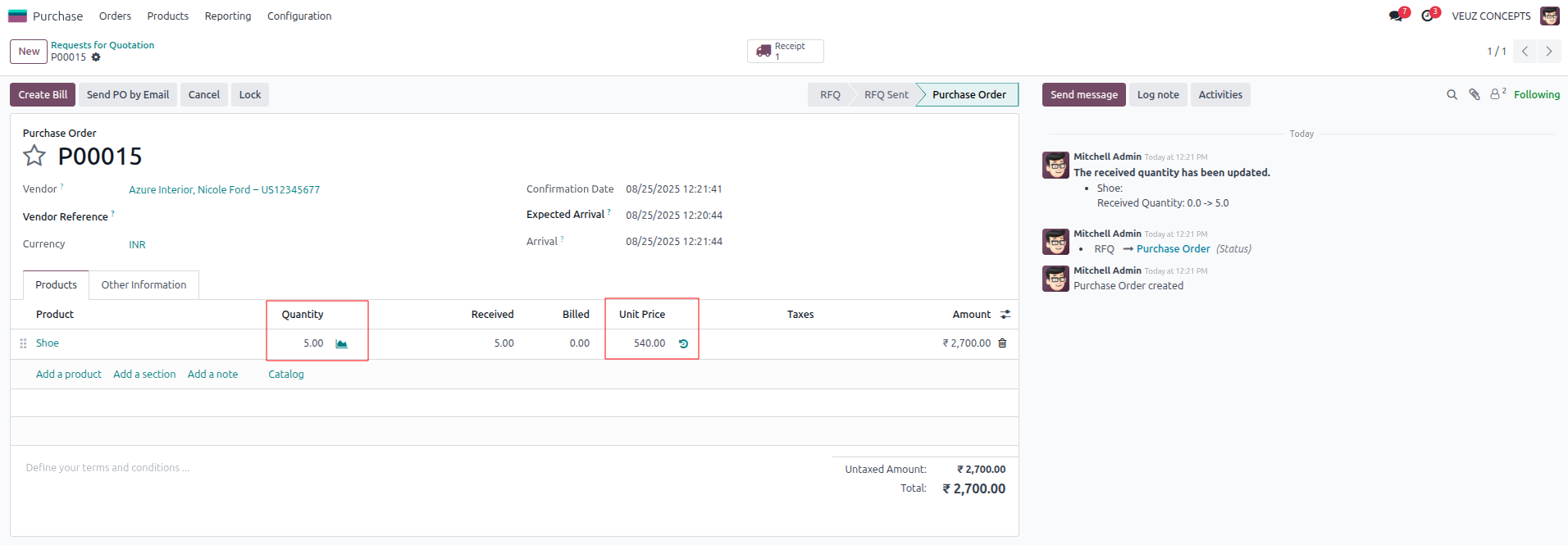
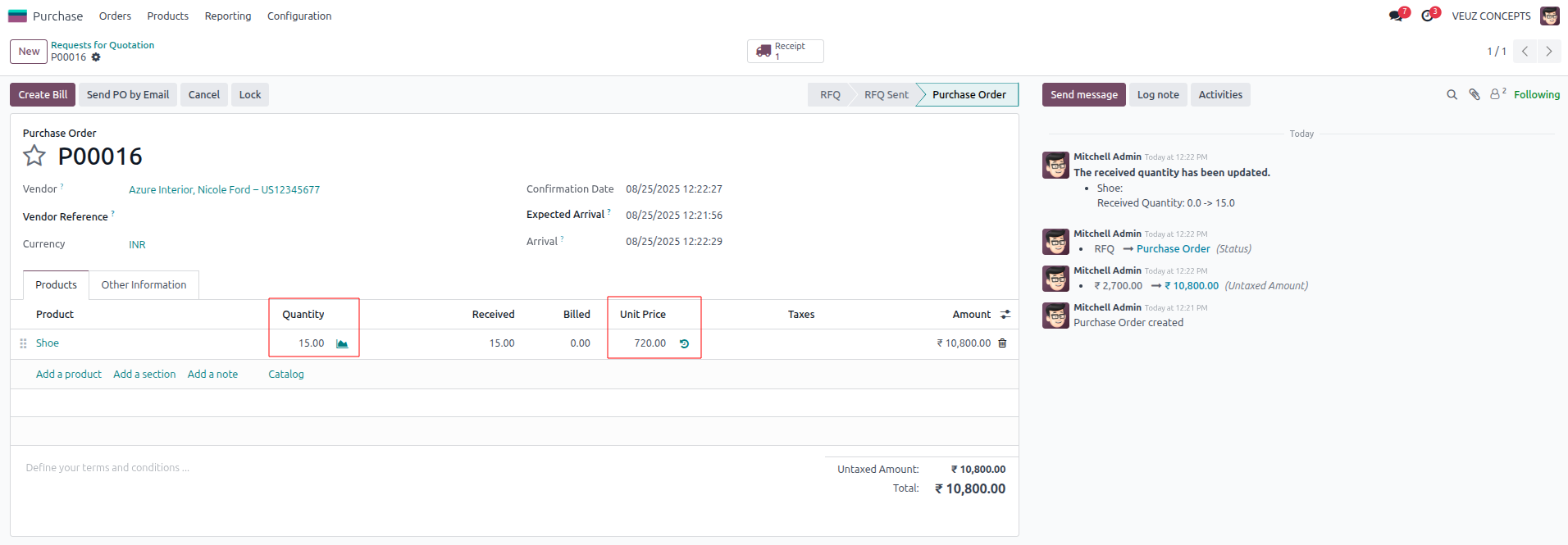
Two purchase orders were created for the product ‘Shoe’ under the category ‘All/FIFO’: the first for 5 units at a price of 540 SR, and the second for 15 units at a price of 720 SR. Now when checking the cost of product it is the average of the purchase cost and quantity.
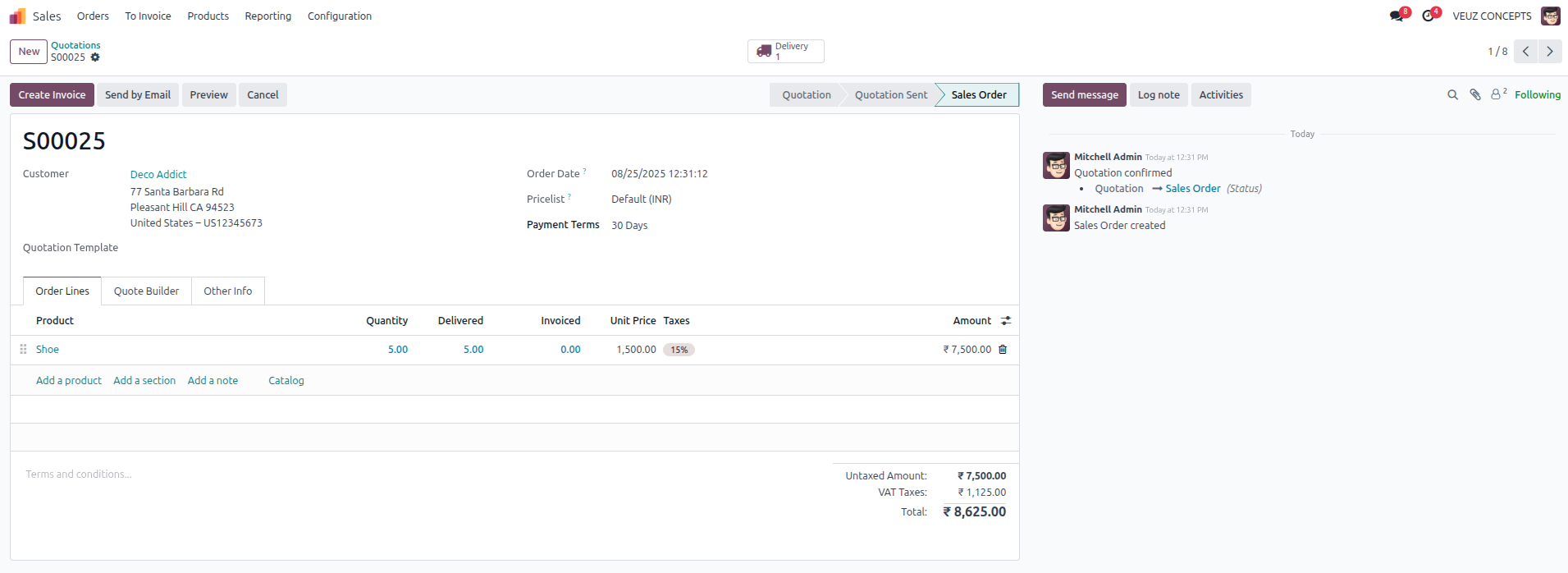
Under this method, stock rotation happens chronologically, with earlier purchases moving out before newer ones. After the first 5 units are sold at 540 SR , the remaining stock is valued at 720 SR per unit, which reflects the cost of the later purchase.
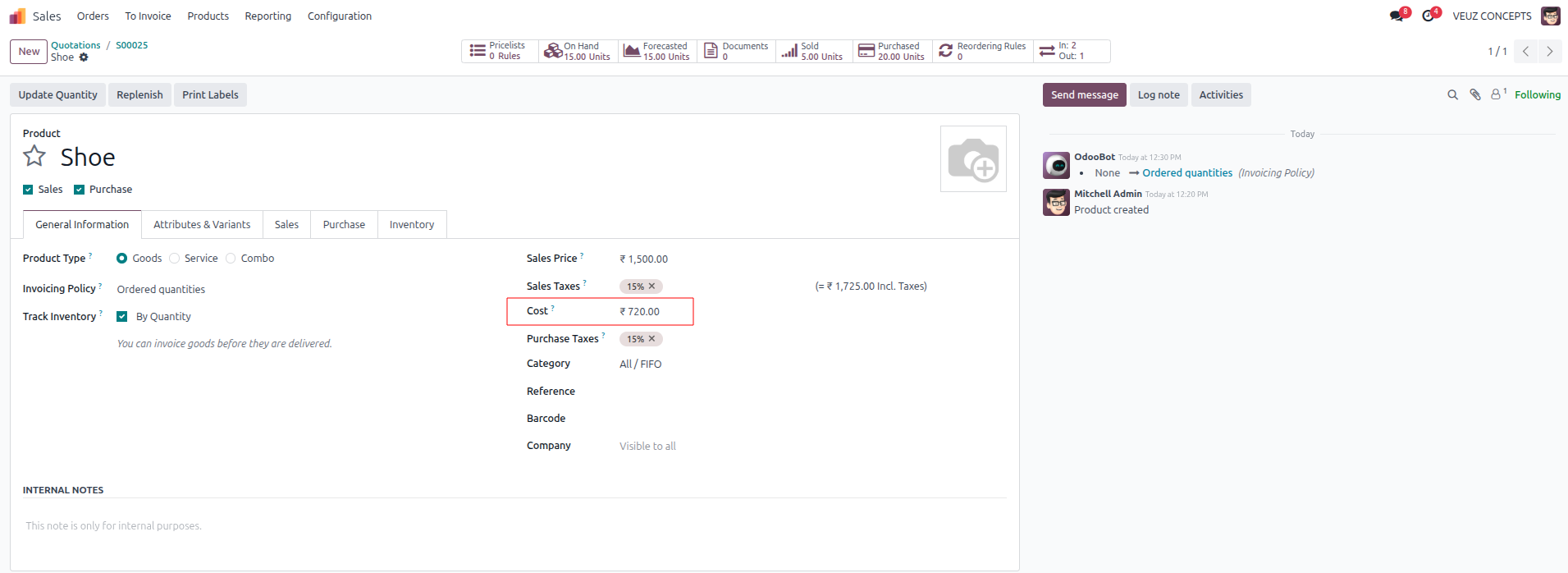
Inventory is valued using the First In, First Out (FIFO) costing method, which assumes that the oldest items are sold first. This means the goods sold are linked to old costs, while the left goods are linked to new costs. Products with a short shelf life or those that must be moved in order of arrival, like food, drinks, medications, and other perishable or time-sensitive items, are best suited for FIFO.









.jpg )







Leave a comment